In the intricate realm of web security, SSL (Secure Socket Layer) emerges as the unsung hero, providing a vital layer of protection for online interactions. Delve into the world of SSL decoding to understand its significance, implementation, and the shield it offers against digital vulnerabilities.
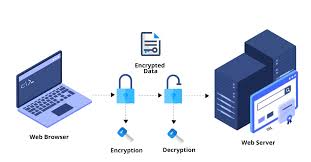
**1. Understanding SSL:
- Essence: SSL is a protocol that establishes secure and encrypted communication between a user’s browser and a website’s server.
- Significance: Protects sensitive information from potential threats during data transmission.
2. Encryption Essentials:
- Functionality: SSL employs encryption algorithms to scramble data, ensuring that it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Security: Safeguards user data, such as login credentials, personal details, and financial information.
3. SSL Certificates:
- Requirement: Websites obtain SSL certificates from Certificate Authorities (CAs).
- Verification: Certificates verify the legitimacy of the website, assuring users that they are interacting with the intended site and not a malicious entity.
4. HTTPS: The Secure Protocol:
- Transition: SSL transforms standard HTTP into HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure).
- Indication: The presence of “HTTPS” in the URL signifies a secure connection, visible to users through the padlock icon.
5. Trust and Credibility:
- User Perception: SSL enhances user trust by assuring them of a secure and encrypted connection.
- Search Engine Impact: Search engines may prioritize secure websites, influencing rankings for improved visibility.
6. Data Integrity Assurance:
- Role: SSL not only encrypts data but also ensures its integrity during transmission.
- Prevention: Guards against data tampering or unauthorized modifications during transit.
7. Extended Validation (EV) Certificates:
- Level of Assurance: EV certificates provide the highest level of validation, requiring a rigorous verification process.
- Visual Indication: Displays the organization’s name in the address bar, instilling additional confidence in users.
8. Mixed Content Risks:
- Concern: Mixed content occurs when both secure (HTTPS) and non-secure (HTTP) elements are present on a page.
- Mitigation: SSL prevents mixed content issues, ensuring a fully secure browsing experience.
9. Browser Security Indicators:
- Visual Signals: Browsers display visual indicators, such as a padlock or a green address bar, to signify a secure connection.
- User Guidance: Helps users identify secure websites and make informed decisions about their online interactions.
10. Mobile Security: – Critical for Apps: SSL is essential for securing data transmission in mobile applications. – Mobile Browser Security: Ensures the same level of security for users accessing websites via mobile browsers.
11. SSL/TLS Protocols: – Evolution: SSL has evolved into TLS (Transport Layer Security), with newer versions providing enhanced security features. – Upgrade Recommendations: Regularly update to the latest TLS versions to benefit from improved security measures.
12. Renewal and Maintenance: – Validity Period: SSL certificates have a specific validity period. – Regular Renewal: Timely renewal is crucial to maintaining continuous security on the website.
13. PCI DSS Compliance: – Requirement: SSL is a fundamental component for compliance with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). – Secure Transactions: Ensures the secure transmission of payment data during online transactions.
14. SNI (Server Name Indication): – Functionality: Allows multiple SSL certificates to be hosted on a single IP address. – Practicality: Particularly beneficial for shared hosting environments.
15. Future of Web Security: – Emerging Technologies: Continuous advancements in web security, including TLS improvements and quantum-resistant cryptography. – Adaptability: Websites need to stay abreast of evolving security measures to counter emerging threats.
By decoding the significance of SSL, website owners can fortify their digital domains against potential threats, instill user confidence, and contribute to the establishment of a secure and trustworthy online environment.









